Sleep is essential for health, yet millions of people around the world struggle with insomnia, a common sleep disorder that affects both physical and mental well-being. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), approximately one in three adults report not getting enough sleep regularly. Chronic insomnia not only impacts daily functioning but also increases the risk of long-term health conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and depression.
🔎 What Is Insomnia?
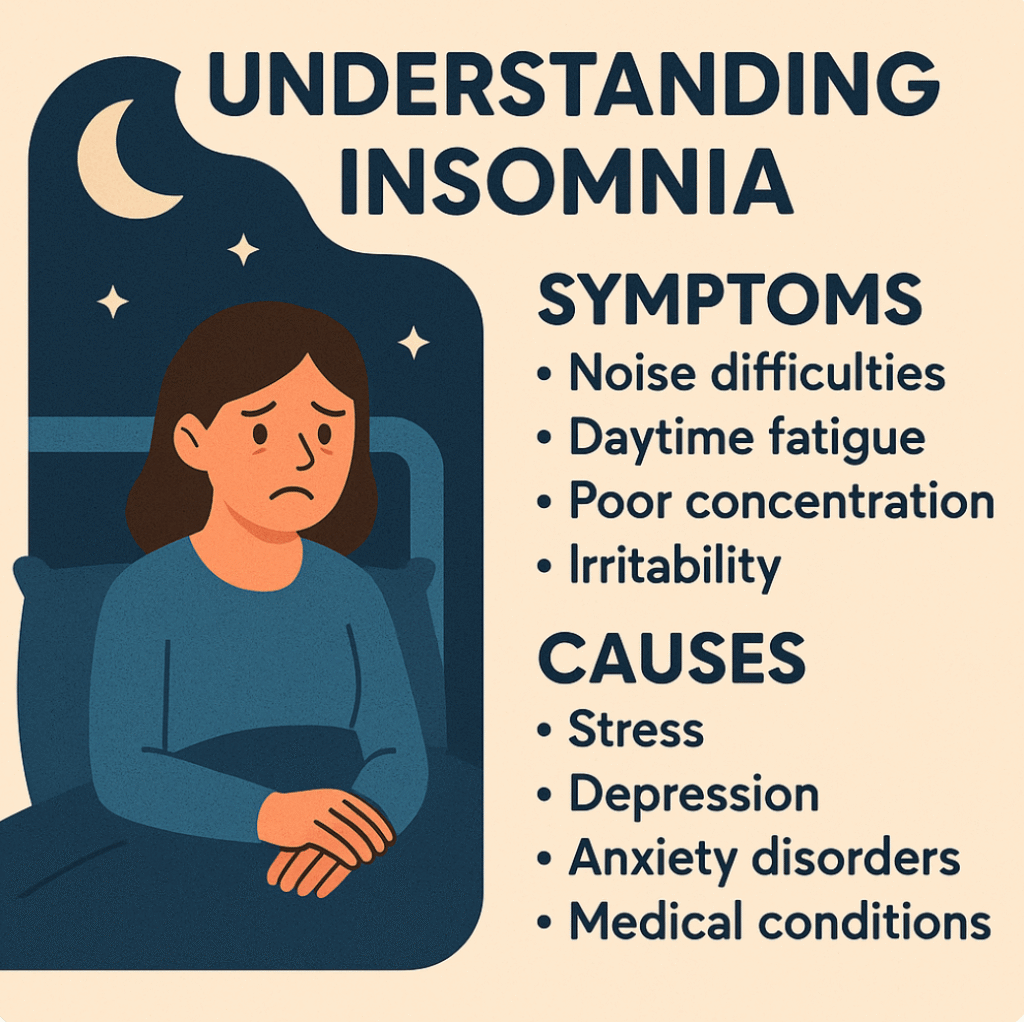
Insomnia is characterized by persistent difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up too early without being able to return to sleep. It can be short-term (acute) or long-term (chronic).
Key Symptoms:
- Trouble falling asleep despite being tired
- Frequent night awakenings
- Daytime fatigue and drowsiness
- Difficulty concentrating or remembering things
- Mood disturbances such as irritability or anxiety
🧠 Common Causes of Insomnia
- Stress: Work pressure, financial issues, or personal challenges can overstimulate the brain, making it difficult to sleep.
- Mental Health Disorders: Depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) are strongly linked with sleep problems.
- Medical Conditions: Chronic pain, asthma, GERD, or thyroid problems often disrupt rest.
- Lifestyle Factors: Excessive caffeine, alcohol, late-night screen use, and irregular sleep schedules interfere with circadian rhythms.
- Environmental Factors: Noise, uncomfortable bedding, or a poor sleep environment can also contribute.
⚠️ Health Risks Associated with Insomnia
Chronic insomnia isn’t just about poor sleep — it can have serious consequences:
- Weakened immune system (making the body more vulnerable to illness)
- Cardiovascular issues (including high blood pressure and heart disease)
- Obesity and diabetes (due to disrupted metabolism and appetite regulation)
- Mental health decline (higher risk of depression, anxiety, and burnout)
🌿 Evidence-Based Strategies to Improve Sleep
- Sleep Hygiene Practices
- Stick to a consistent bedtime and wake-up time.
- Limit screen exposure an hour before bed.
- Avoid caffeine or heavy meals late at night.
- Optimize the Sleep Environment
- Keep your bedroom cool, dark, and quiet.
- Invest in a comfortable mattress and pillow.
- Relaxation Techniques
- Meditation, deep breathing, or progressive muscle relaxation reduce stress.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I)
- A scientifically proven method to change sleep-related thoughts and behaviors.
- Medical Support
- If insomnia persists, consult a healthcare provider. Sometimes short-term use of sleep aids may be necessary under medical supervision.
🌍 Helpful Resources
🇰🇷 Premium Korean Ginseng Online Shop