Vitamin D, often called the “sunshine vitamin,” is essential for strong bones, immune function, and overall health. Yet, despite its importance, vitamin D deficiency is surprisingly common worldwide, affecting more than 1 billion people according to global health estimates. This article explores the symptoms, causes, and prevention strategies for vitamin D deficiency, providing actionable insights backed by medical research.
🧬 Why Vitamin D Matters
Vitamin D is unique because it functions as both a vitamin and a hormone. Its primary role is to regulate calcium and phosphorus, which are crucial for bone strength. Beyond skeletal health, vitamin D contributes to:
- Immune support: Helps fight infections and regulate immune responses.
- Muscle function: Prevents weakness and supports mobility.
- Mental health: Low vitamin D has been linked to depression and mood disorders.
- Chronic disease prevention: Adequate levels may lower the risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain cancers.
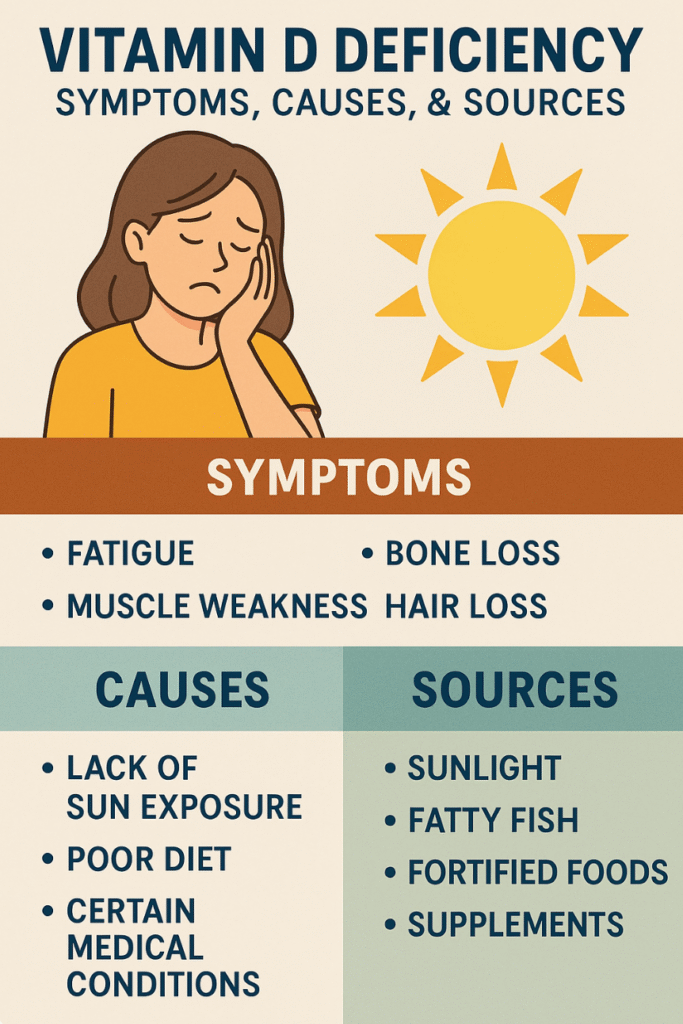
⚠️ Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency
Deficiency often goes unnoticed until it causes health problems. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent fatigue
- Muscle weakness
- Bone pain or frequent fractures
- Hair loss
- Increased risk of infections
Severe, prolonged deficiency may lead to osteomalacia in adults (soft bones) or rickets in children (bone deformities).
🔎 Causes of Vitamin D Deficiency
Several factors contribute to low vitamin D levels:
- Limited sun exposure: Living in northern latitudes, wearing sunscreen constantly, or staying indoors reduces natural vitamin D production.
- Dietary insufficiency: Few foods naturally contain vitamin D, making deficiency more likely in populations with limited access to fortified foods.
- Medical conditions: Disorders such as celiac disease, kidney disease, and obesity can impair absorption and metabolism.
- Skin pigmentation: Darker skin produces less vitamin D from sunlight compared to lighter skin tones.
🥗 How to Improve Vitamin D Levels
- Sunlight: Expose your skin to sunlight for 10–30 minutes several times a week, depending on skin tone and location.
- Dietary sources: Eat fatty fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel), egg yolks, and fortified foods (milk, cereals, orange juice).
- Supplements: Vitamin D3 supplements are often recommended, particularly in winter or for at-risk groups.
- Regular testing: A simple blood test can determine vitamin D status and guide supplementation.
🌍 Global Health Relevance
Vitamin D deficiency is now considered a worldwide public health issue. The World Health Organization (WHO) highlights its role in bone health and chronic disease prevention. Awareness campaigns encourage populations to balance sun safety with adequate vitamin D exposure.
For additional trusted resources:
✅ Conclusion
Vitamin D deficiency is silent but impactful. By recognizing the symptoms, addressing the causes, and taking proactive steps to improve levels, individuals can strengthen bones, support immunity, and enhance long-term health.
🇰🇷 Premium Korean Ginseng Online Shop