As we age, our nutritional needs evolve. The body requires fewer calories but more nutrients to maintain strength, support immunity, and prevent chronic disease. Proper nutrition becomes essential to preserve energy, muscle mass, bone density, and cognitive health in older adulthood. This comprehensive guide explores the science-backed dietary strategies that help seniors thrive with vitality and grace.
🌿 Why Nutrition Matters in Older Age
Aging brings physiological changes that affect appetite, digestion, and metabolism. The body’s ability to absorb nutrients—such as vitamin B12, calcium, and vitamin D—diminishes, while muscle mass and hydration levels decline. Without conscious adjustments to diet, these changes can lead to malnutrition, fatigue, or increased risk of illness.
Proper nutrition is not just about living longer; it’s about living better—maintaining independence, energy, and mental clarity through mindful eating habits.
🍎 Key Components of a Healthy Senior Diet
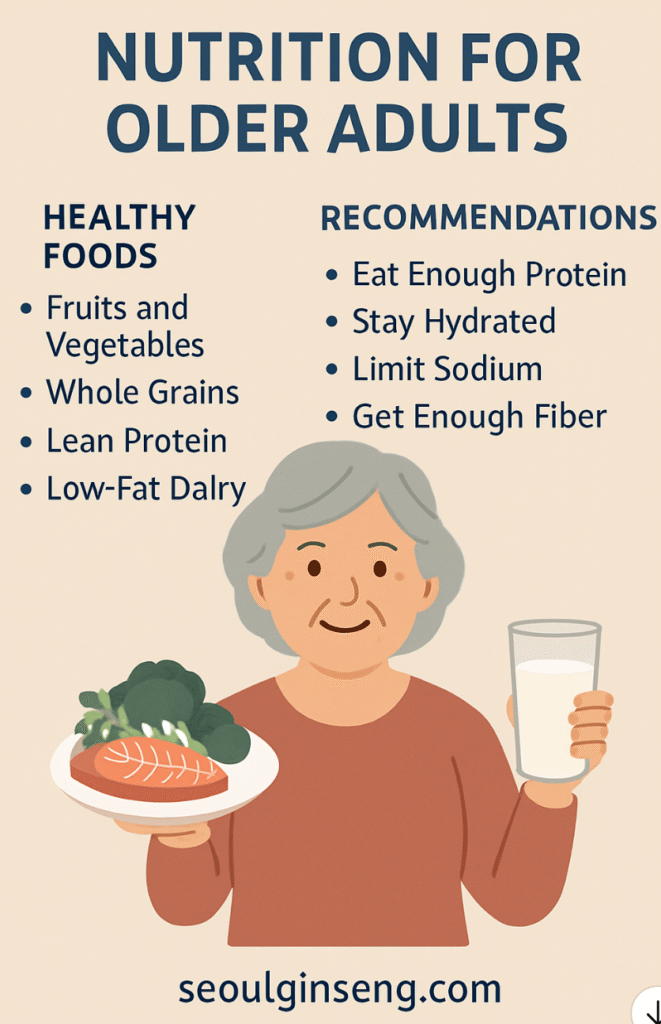
1. Fruits and Vegetables
Rich in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber, fruits and vegetables strengthen the immune system and promote digestive health. Aim for a colorful plate—each hue represents a unique nutrient profile (e.g., orange for beta-carotene, green for folate).
2. Whole Grains
Whole grains such as oats, quinoa, brown rice, and barley support heart health and stabilize blood sugar levels. They also provide essential B vitamins for energy metabolism.
3. Lean Protein
Protein helps maintain muscle strength and repair tissues. Include fish, poultry, beans, tofu, and eggs. For those with chewing difficulties, soft proteins like yogurt or lentils are excellent alternatives.
4. Low-Fat Dairy
Calcium and vitamin D are vital for bone health. Choose low-fat milk, yogurt, or fortified plant-based alternatives to prevent osteoporosis.
💧 Additional Dietary Recommendations
- Eat Enough Protein: Older adults need more protein per body weight to counteract muscle loss (sarcopenia).
- Stay Hydrated: Aging reduces thirst sensation; aim for 6–8 glasses of water daily.
- Limit Sodium: Excess salt contributes to high blood pressure. Flavor meals with herbs instead.
- Get Enough Fiber: Fiber prevents constipation and supports heart health. Whole grains, vegetables, and legumes are excellent sources.
⚕️ Managing Common Nutrition Challenges
1. Loss of Appetite
Enhance flavor naturally with herbs and mild spices. Small, frequent meals can help maintain calorie intake.
2. Difficulty Chewing or Swallowing
Opt for softer foods such as soups, smoothies, or mashed vegetables. Regular dental checkups can also improve comfort during eating.
3. Medication Interactions
Some prescriptions interfere with nutrient absorption (e.g., diuretics and potassium loss). Consult healthcare professionals for safe dietary adjustments.
4. Digestive Changes
Reduced stomach acid can affect vitamin absorption. Consider foods rich in B12 and probiotics for gut health.
🌞 Long-Term Benefits of Proper Nutrition
Balanced nutrition supports:
- Stronger bones and muscles
- Reduced risk of chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease
- Improved memory and mental focus
- Better skin health and vitality
- Enhanced emotional well-being and longevity
Healthy aging begins at the table—nourish your body with care and consistency.
🇰🇷 Premium Korean Ginseng Online Shop