Introduction: Your Brain Runs on Blood, Not Just Ideas
We often think of focus, creativity, and mental clarity as purely “brain-based” qualities — as if cognition floats in space, separate from the body. But the truth is far more biological and far more fascinating:
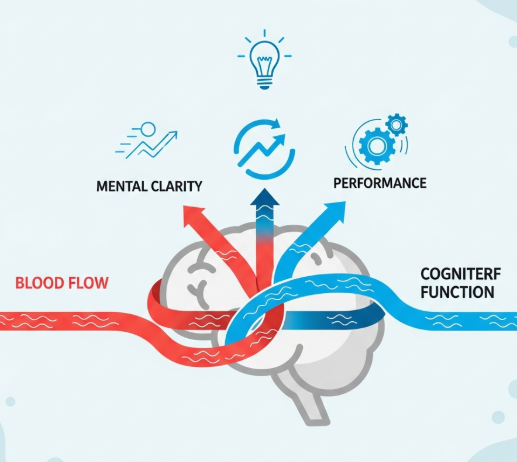
🧠 Your brain is an energy-hungry organ — and it depends almost entirely on circulation to function.
Every thought, every memory, every decision is powered by a steady flow of oxygen-rich blood. When circulation is compromised — even subtly — brain fog, fatigue, slow thinking, poor recall, and low motivation are often the first signs.
Cognitive performance is not just about intelligence.
It is about delivery systems, vascular health, and microcirculation.
1. The Brain’s Hidden Metabolic Demands
Though it makes up only ~2% of your body weight, the brain consumes:
- 20% of all oxygen
- 25% of all glucose
- More blood flow than any other organ
It has no storage system for energy, meaning it requires constant oxygen delivery to maintain:
- Focus
- Memory
- Learning
- Emotional regulation
- Executive decision-making
Even slight circulation inefficiency = noticeable cognitive decline.
2. How Circulation Affects Mental Performance
🔹 Poor circulation → oxygen deficit → slower neuronal firing
Result: brain fog, sluggish recall, reduced creativity
🔹 Reduced blood flow → lower nutrient delivery
Result: fatigue, mood swings, decreased motivation
🔹 Microvascular stagnation → inflammation + oxidative stress
Result: faster cognitive aging + stress sensitivity
Cognition doesn’t fail randomly.
It deteriorates when it is under-supplied.
3. Why Mental Fatigue Often Begins in the Bloodstream
You may think you’re tired from “too much thinking.”
In reality, your brain is starved for energy.
Mental workload increases oxygen demand.
If circulation cannot keep up, the brain moves into protective slowdown mode:
- You can’t form sentences properly
- You reread the same paragraph
- You lose your train of thought
- You feel “mentally heavy”
This is not laziness.
It’s a supply problem.
4. Signs Your Brain Needs Better Circulation
You may experience:
✔ Frequent yawning while concentrating
✔ Cold hands and feet
✔ Difficulty waking up mentally
✔ Slow recall or “tip of the tongue” moments
✔ Tension headaches
✔ Mental exhaustion despite minimal tasks
✔ Lack of mental stamina
These are vascular signals, not just psychological ones.
5. How to Improve Brain Circulation Naturally
1. Move — even slightly
Sitting still reduces cerebral blood flow by up to 40%.
Micro-movement, stretching, walking = circulation activation.
2. Breathe consciously
Shallow breathing lowers oxygenation.
Deep breathing increases cerebral perfusion within seconds.
3. Strengthen the vascular system
Hydration, mineral intake, omega-3s, polyphenols, nitric oxide–supportive foods (beets, leafy greens, pomegranate) all help improve blood vessel elasticity.
4. Release tension from neck and jaw
Tight muscles restrict carotid blood flow.
Massage, stretching, heat therapy are simple but effective.
5. Restore sleep quality
During deep sleep, blood flow shifts to the brain to clear toxins and repair neurons. Poor sleep = poor cognitive circulation.
6. Support microcirculation
Traditional herbs such as Korean red ginseng, ginkgo, and adaptogens are studied for their role in supporting blood flow and oxygen delivery — especially to the brain.
6. A Healthy Brain Is a Circulating Brain
The next era of brain health is not just about supplements, nootropics, or “hacking” focus — it is about restoring the biological foundation of thought:
Blood flow.
Circulation is cognition.
Microcirculation is clarity.
Your ideas are only as powerful as the oxygen fueling them.