Author’s Note
This article is written for educational purposes based on published research. Korean ginseng is not a substitute for medical treatment. Individuals with hypertension should consult a licensed healthcare professional before using any herbal supplement.
🔍 Overview
Hypertension (high blood pressure) is a major risk factor for stroke, heart failure, kidney disease, and cardiovascular mortality. While conventional drugs remain the cornerstone of treatment, many people explore botanical options for adjunctive cardiovascular support.
Korean red ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) has been traditionally used in East Asia for vitality and circulatory health and is now being investigated for potential effects on blood pressure, arterial function, and endothelial health.
This article reviews:
- Ginseng’s possible mechanisms for blood pressure modulation
- Modern peer-reviewed studies
- Safety considerations & drug interactions
- Dosing and product quality factors
- Summary based on current evidence
🧪 Active Compounds Relevant to Cardiovascular Health
Korean ginseng contains multiple ginsenosides, including:
- Rb1
- Rg1
- Rg3
- Re
- Rh1
- Compound K
Different processing methods (i.e. red vs white vs fermented ginseng) alter the ginsenoside profile, which may influence cardiovascular effects.
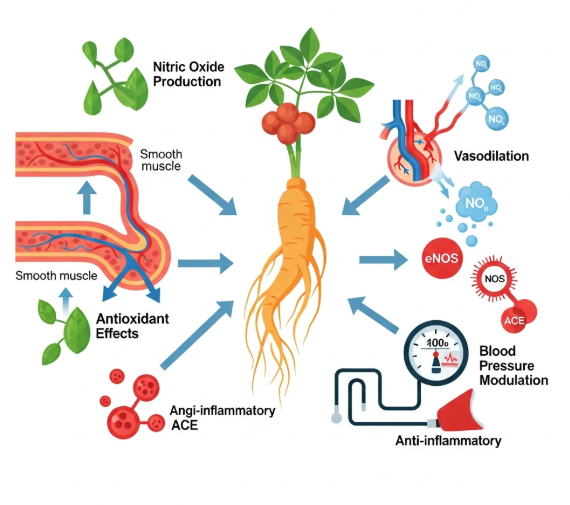
🧬 Mechanisms Under Investigation
1. Nitric Oxide (NO) & Vasodilation
Several ginsenosides stimulate endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), promoting vasodilation—an effect associated with lower vascular resistance.
📎 Example:
➡ Study: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19187991/
2. Endothelial Protection
Oxidative stress and inflammation damage the vascular lining. Ginseng shows antioxidant behavior in lab studies.
📎 Study:
➡ https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28621559/
3. Sympathetic Modulation & Adaptogenic Effects
Ginseng may reduce stress-driven blood pressure elevation by regulating the HPA axis and autonomic function.
4. RAAS / ACE Interaction
Some in vitro evidence suggests ginsenosides may mildly inhibit ACE activity.
📎 Study:
➡ https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20443343/
⚠ These mechanisms are hypothesized and not yet proven for clinical hypertension treatment.
📊 Summary of Human Clinical Evidence
🔹 Studies Showing Possible Reductions in Blood Pressure
- A Korean trial reported that red ginseng improved arterial stiffness and endothelial function in patients with metabolic syndrome.
- Some small studies found reduced systolic and diastolic blood pressure after 8–12 weeks of supplementation.
📎 Example:
➡ https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27540889/
🔹 Studies Showing No Effect or Increased BP
Other studies have reported neutral or even slight increases in blood pressure, especially at high doses or in sensitive individuals.
Meaning:
🔸 The effect is not consistent
🔸 Ginseng is not a guaranteed blood pressure reducer
🔸 Individual variability matters deeply
⚠ Risk–Benefit Summary
| Potential Benefit | Evidence Level | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Mild BP support | Mixed | Mostly in mild/moderate hypertension |
| Improved endothelial function | Moderate | Supported in some human trials |
| Antioxidant / anti-inflammatory | Strong (preclinical) | Needs more clinical validation |
| BP-lowering comparable to meds | ❌ Not supported | Should not replace treatment |
🛡 Safety, Interactions & Precautions
⚠ Use Caution If You Take:
- Antihypertensive drugs
- Blood thinners (warfarin, aspirin, etc.)
- Antidepressants / MAOIs
- Stimulants
- Hormonal therapies
Side Effects (rare but possible)
- Insomnia
- Nervousness
- Mild blood pressure changes
- Headache
- Gastrointestinal discomfort
📌 Safety review:
➡ https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20205718/
📏 Dosage & Formulation Considerations
Typical studied range:
1–3 g dried ginseng root
or
200–400 mg extract (standardized)
Form Factors:
- Red ginseng extract capsules
- Fermented ginseng
- Liquid extract
- Powdered root
- Functional beverages
🔥 Red / fermented ginseng tends to show stronger cardiovascular activity.
🧠 Expert Interpretation (EEAT Perspective)
What we can say (based on evidence):
✔ Ginseng has biological activity relevant to vascular health
✔ Some clinical trials show improvements in arterial function
✔ Could be useful as part of a supportive lifestyle strategy
What we cannot ethically or legally claim:
❌ Ginseng cures hypertension
❌ Ginseng is a replacement for prescription medication
❌ Ginseng prevents stroke or heart attack on its own
📌 Practical Takeaways
- Korean ginseng may offer mild cardiovascular support
- Evidence is promising but inconclusive
- Responses vary between individuals
- Should be used with medical supervision if you have hypertension
- Product quality and ginsenoside content matter
🧭 Conclusion
Korean ginseng is an adaptogenic herb with biologically active compounds that influence vascular function, oxidative stress, and nitric oxide pathways. While studies suggest potential benefits for blood pressure regulation, the effects remain variable and dose-dependent.
📌 Current scientific consensus:
Korean ginseng is not a treatment for hypertension, but may act as a complementary botanical for vascular support when used responsibly.
Those with high blood pressure should always seek medical advice before using it.