Chronic stress is one of the most pervasive health challenges of modern life. Whether caused by demanding careers, financial pressure, or digital overload, persistent stress elevates cortisol, the body’s primary stress hormone. While cortisol plays an essential role in survival—regulating energy, metabolism, and alertness—continuously elevated cortisol disrupts nearly every biological system, increasing the risk of fatigue, sleep disorders, weight gain, hypertension, and impaired cognition.
This article provides an in-depth, scientifically grounded exploration of effective cortisol-regulation methods and examines how Korean ginseng (Panax ginseng) supports the endocrine and nervous systems under chronic stress.
Understanding Cortisol: The Body’s Stress Signal
Cortisol is produced by the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, a complex system linking the brain and adrenal glands. Under acute stress, cortisol rises to help the body:
- Mobilize glucose for quick energy
- Increase alertness
- Regulate blood pressure
- Strengthen short-term inflammatory responses
However, chronic stress keeps the HPA axis switched “on”, resulting in dysregulated cortisol patterns:
- High cortisol all day → anxiety, insomnia, abdominal fat, irritability
- Low morning cortisol → fatigue, brain fog, low motivation
- Flattened cortisol curve → burnout, emotional exhaustion
Managing stress requires restoring healthy daily cortisol rhythms, not merely lowering cortisol.
Scientific Stress & Cortisol Regulation Methods
1. Circadian Rhythm Synchronization
Cortisol naturally peaks in the morning and declines throughout the day. Improving circadian alignment helps stabilize this rhythm.
Evidence-based strategies:
- Morning sunlight exposure to stimulate cortisol awakening response (CAR)
- Regular wake-sleep cycles
- Avoiding bright screens at night to prevent melatonin suppression
Studies show that circadian entrainment improves cortisol stability and sleep efficiency.
2. Breathwork & Parasympathetic Activation
Breathing exercises activate the vagus nerve, reducing sympathetic arousal.
Effective techniques:
- 4-7-8 breathing
- Slow diaphragmatic breathing (6 breaths/min)
- Box breathing
Clinical data indicates that paced breathing lowers cortisol within minutes and improves heart-rate variability (HRV).
3. Physical Activity
Exercise regulates cortisol in two ways:
- Short-term increase during activity
- Long-term decrease through improved stress resilience
Moderate aerobic exercise (30–45 minutes) reduces cortisol baseline levels and enhances emotional stability.
4. Anti-Inflammatory Diet & Gut Support
Chronic inflammation disrupts HPA axis signaling.
Supportive nutrition includes:
- Omega-3 fatty acids (EPA/DHA)
- Antioxidant-rich foods (berries, greens, turmeric)
- Fermented foods to support the gut–brain axis
A balanced microbiome reduces systemic inflammation, indirectly stabilizing cortisol.
5. Sleep Optimization
Cortisol dysregulation frequently stems from inadequate sleep.
Strategies:
- 7–9 hours of sleep
- Limiting stimulants after noon
- Creating a dark, cool sleep environment
Effective sleep reinforces natural cortisol decline during the night and healthy morning rise.
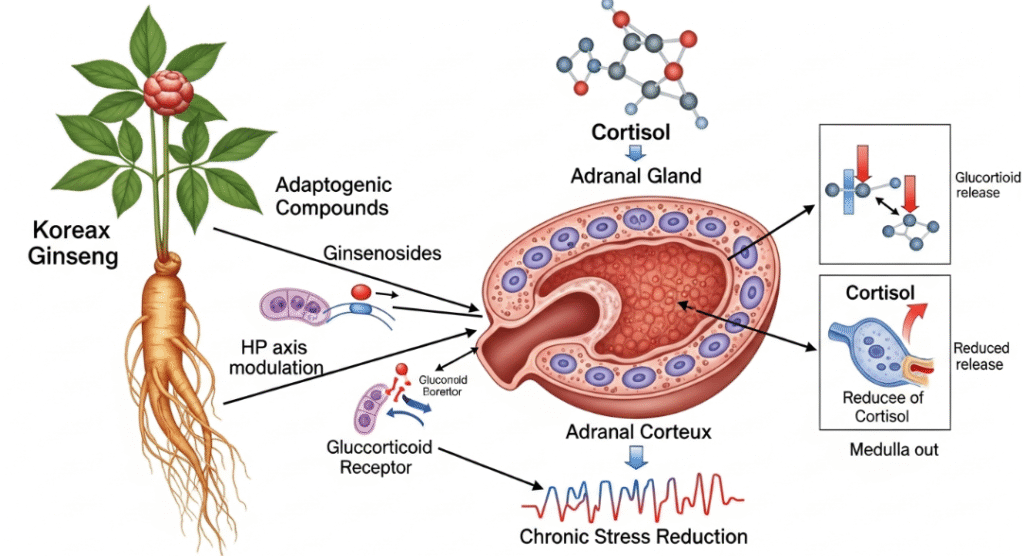
Korean Ginseng: A Natural Cortisol Regulator
Panax ginseng is one of the most extensively studied adaptogens. Its active compounds, ginsenosides, modulate stress response pathways and support endocrine balance.
1. HPA Axis Modulation
Research shows Korean ginseng helps normalize HPA axis signaling by:
- Reducing excessive cortisol secretion
- Enhancing resilience to chronic stress exposure
- Balancing neurotransmitter response (serotonin, dopamine, GABA)
This helps prevent “hyperarousal,” a state commonly associated with anxiety, insomnia, and burnout.
2. Improves Stress Perception and Emotional Stability
Ginseng does not simply suppress cortisol—it improves the brain’s adaptability to stress.
Studies reveal improvements in:
- Mood regulation
- Cognitive clarity
- Reaction to stressors
- Emotional resilience
This makes it valuable for individuals with intense daily demands, such as executives, entrepreneurs, and students.
3. Anti-inflammatory & Antioxidant Effects
Chronic stress elevates inflammation, which further disrupts cortisol rhythms.
Ginseng’s ginsenosides:
- Reduce oxidative stress
- Support immune function
- Protect against stress-related cellular damage
This reduces the biological burden that typically raises cortisol levels.
4. Enhances Sleep Quality
Cortisol imbalance causes insomnia; conversely, poor sleep keeps cortisol elevated.
Ginseng may:
- Reduce nighttime cortisol spikes
- Improve non-REM sleep quality
- Support melatonin regulation indirectly through stress reduction
This strengthens natural hormonal rhythms over time.
How to Integrate Korean Ginseng Into Cortisol Regulation
For best results:
Morning (Optimal Timing)
- 1–2 capsules or recommended dose of Korean red ginseng
- Supports cortisol awakening response
- Enhances daytime cognitive performance
Combine with:
- 10 minutes sunlight
- Light movement or stretching
Evening (Avoid High Dose Late at Night)
- If needed, use low-dose formulations for stress relief
- Pair with relaxation techniques (breathwork, warm bath)
Consistency matters:
Adaptogens deliver benefits through cumulative effects over weeks.
Conclusion
Chronic stress and cortisol dysregulation affect mental clarity, metabolic health, immune function, and long-term wellbeing. Science-backed methods—such as circadian alignment, breathwork, sleep optimization, and anti-inflammatory nutrition—provide foundational support.
When combined with premium adaptogens like Korean ginseng, individuals can achieve stronger resilience, improved mood, and more stable cortisol rhythms.
Korean ginseng remains one of the most powerful natural tools for restoring balance in a world where stress is constant.
🇰🇷 Premium Korean Ginseng Online Shop