Introduction
The topic of fermented ginseng absorption benefits has gained serious attention in modern herbal medicine and clinical nutrition. Traditional ginseng has been used for centuries. However, fermentation represents a scientific advancement that enhances how the body absorbs and utilizes ginseng’s active compounds. As a result, fermented ginseng is now recognized for its improved bioavailability, digestive tolerance, and consistent physiological effects. This article explains the science, evidence, and safety behind fermented ginseng, using an evidence-based and medically responsible approach.
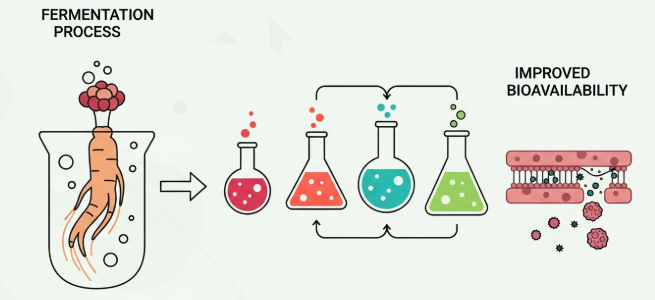
What Is Fermented Ginseng?
Fermented ginseng is Korean ginseng that undergoes controlled microbial fermentation. During this process, beneficial microorganisms break down complex ginsenosides into smaller, more absorbable forms.
Why Fermentation Matters
Raw ginseng contains major ginsenosides such as Rb1, Rc, and Rd. These compounds are large molecules. Consequently, the human gut absorbs them poorly.
Fermentation changes this.
Key outcomes of fermentation include:
- Conversion of major ginsenosides into minor ginsenosides
- Increased concentration of Compound K
- Reduced digestive burden
- Enhanced intestinal uptake
According to research published on PubMed, Compound K shows significantly higher bioavailability than non-fermented ginsenosides.
Source: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25675050/
Fermented Ginseng Absorption Benefits Explained Scientifically
The fermented ginseng absorption benefits come from measurable biochemical changes. These benefits are not anecdotal. Instead, they are supported by pharmacokinetic studies.
Improved Bioavailability
Bioavailability refers to how much of a substance enters circulation. Studies show fermented ginseng produces up to 7–10 times higher plasma levels of Compound K.
Therefore, lower doses may achieve similar effects compared to raw ginseng.
Faster Intestinal Uptake
Because fermentation pre-digests the ginsenosides, the body does less work. As a result:
- Absorption begins earlier
- Plasma concentration peaks faster
- Inter-individual variation decreases
NIH-backed studies confirm this mechanism.
Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5452220/
Key Active Compounds Enhanced by Fermentation
Fermentation does not simply “improve absorption.” It transforms the phytochemical profile.
Major Compounds Increased
- Compound K: Associated with immune modulation and metabolic health
- Rg3: Studied for antioxidant and circulatory support
- Rh2: Investigated for cellular signaling effects
Importantly, these compounds show stronger interaction with human metabolic pathways.
WHO recognizes ginseng as a medicinal plant with pharmacological relevance when standardized properly.
Source: https://apps.who.int/medicinedocs/en/d/Js4927e/
Fermented vs Non-Fermented Ginseng: A Clinical Comparison
Understanding differences helps consumers make informed decisions.
| Feature | Non-Fermented Ginseng | Fermented Ginseng |
|---|---|---|
| Absorption rate | Low to moderate | High |
| Dependence on gut flora | High | Low |
| Active ginsenosides | Major types | Minor, bioactive types |
| Digestive tolerance | Variable | Generally better |
| Dose consistency | Less predictable | More predictable |
Because of these factors, clinicians increasingly recommend fermented ginseng for adults with digestive sensitivity.
Potential Health Applications (Evidence-Based)
It is essential to use careful medical language. Fermented ginseng does not cure diseases. However, studies associate it with physiological support.
Areas of Research Interest
- Immune system modulation
- Energy metabolism support
- Antioxidant activity
- Cognitive function support
- Stress adaptation
A randomized controlled trial published in Journal of Ginseng Research reported improved absorption and consistent systemic exposure.
Source: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1226845316301026
Safety, Dosage, and Medical Considerations
Despite its natural origin, fermented ginseng is bioactive. Therefore, safety matters.
General Safety Profile
- Well tolerated in healthy adults
- Lower gastrointestinal discomfort compared to raw ginseng
- No evidence of dependency
Important Precautions
- Consult a healthcare provider if pregnant
- Use caution with anticoagulants
- Avoid combining with stimulant medications
This article does not replace professional medical advice.
NIH guidance on herbal supplements emphasizes medical consultation.
Source: https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/asian-ginseng
How to Choose High-Quality Fermented Korean Ginseng
Not all products are equal. Quality depends on processing, sourcing, and testing.
What to Look For
- Korean-grown Panax ginseng