Introduction
Diabetes symptoms are often subtle at first, yet they can signal serious metabolic changes in the body. Many people overlook early signs because they develop gradually and may seem harmless. However, recognizing these symptoms early is critical. Early awareness allows timely diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and prevention of long-term complications. This article explains diabetes symptoms in a clear, evidence-based manner, following international medical guidance and current scientific research.
What Is Diabetes and Why Symptoms Appear
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by high blood glucose levels. It occurs when the body cannot produce enough insulin or cannot use insulin effectively. Insulin is essential for moving glucose from the bloodstream into cells for energy.
As a result, glucose accumulates in the blood. Over time, this imbalance affects multiple organs. Consequently, specific symptoms begin to appear. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), diabetes is one of the fastest-growing global health challenges today.
Source: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes
Common Diabetes Symptoms to Watch For
Many diabetes symptoms are shared across type 1 and type 2 diabetes. However, their severity and onset can differ.
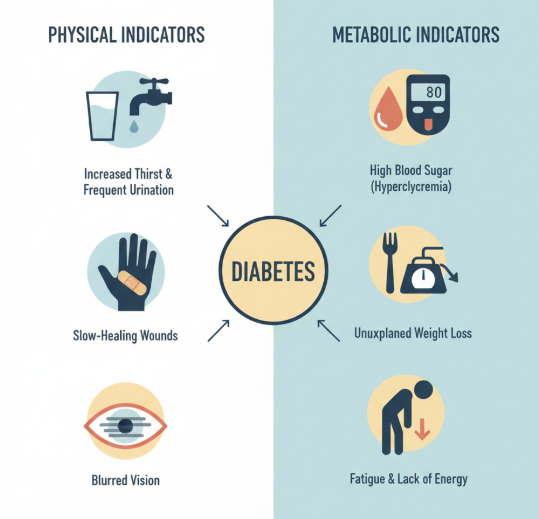
Frequent Urination and Excessive Thirst
High blood sugar forces the kidneys to work harder. Therefore, excess glucose is excreted in urine. This process pulls water from the body.
As a result:
- Urination becomes more frequent
- Persistent thirst develops
- Dehydration may occur
These signs are often among the earliest diabetes symptoms.
Unexplained Weight Loss
Despite eating normally or more than usual, some people lose weight. This happens because the body cannot use glucose efficiently. Instead, it breaks down fat and muscle for energy.
This symptom is more common in type 1 diabetes. Still, it can occur in advanced type 2 diabetes.
Fatigue and Low Energy
When glucose cannot enter cells, energy production declines. Therefore, chronic tiredness develops. Fatigue often interferes with daily activities and concentration.
Less Obvious but Clinically Important Symptoms
Some diabetes symptoms are frequently overlooked. However, they may indicate ongoing tissue damage.
Blurred Vision
High blood glucose can alter fluid levels in the eyes. Consequently, the lens swells and vision becomes blurry. In most cases, vision improves once blood sugar stabilizes.
The National Eye Institute highlights diabetes as a leading cause of vision impairment.
Source: https://www.nei.nih.gov/learn-about-eye-health/eye-conditions-and-diseases/diabetic-eye-disease
Slow Wound Healing and Frequent Infections
Elevated glucose weakens immune function. In addition, blood circulation may decline. As a result:
- Cuts heal slowly
- Skin infections recur
- Gum disease becomes more common
These signs suggest long-term blood sugar imbalance.
Diabetes Symptoms in Men and Women: Key Differences
While many symptoms overlap, some differences exist.
In Men
- Reduced libido
- Erectile dysfunction
- Muscle weakness
These issues are often linked to nerve and blood vessel damage.
In Women
- Recurrent urinary tract infections
- Vaginal yeast infections
- Hormonal irregularities
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), hormonal changes can influence symptom expression.
Source: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes
Early Diabetes Symptoms vs. Advanced Warning Signs
Early-stage symptoms are often mild. However, advanced signs indicate more serious complications.
Early indicators include:
- Mild fatigue
- Increased thirst
- Slight vision changes
Advanced warning signs include:
- Numbness or tingling in hands and feet
- Persistent infections
- Chest pain or shortness of breath
At this stage, medical intervention becomes urgent.
How Diabetes Is Diagnosed Clinically
Diagnosis does not rely on symptoms alone. Blood tests are essential.
Common diagnostic tools include:
- Fasting plasma glucose test
- HbA1c test
- Oral glucose tolerance test
The American Diabetes Association provides standardized diagnostic criteria.
Source: https://diabetes.org/about-diabetes/diagnosis
Early testing is recommended for individuals with risk factors such as obesity, family history, or sedentary lifestyle.
Role of Nutrition and Herbal Support in Symptom Management
Lifestyle plays a crucial role in managing diabetes symptoms. Balanced nutrition, physical activity, and medical therapy remain foundational.
Evidence-Based Herbal Considerations
Certain herbs have been studied for metabolic support. Korean ginseng, for example, has been researched for its potential role in glucose metabolism.
Scientific reviews published on PubMed suggest that ginsenosides may influence insulin sensitivity. However, results vary, and herbs should never replace prescribed medication.
Source: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31401298/
Always consult a healthcare professional before using herbal supplements.
When to See a Doctor
Medical consultation is essential if symptoms persist or worsen. Early diagnosis reduces the risk of complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, and neuropathy.
Seek immediate care if:
- Symptoms appear suddenly
- Weight loss is rapid
- Vision changes are severe
Professional evaluation ensures safe and effective management.
Conclusion
Diabetes symptoms serve as critical signals of metabolic imbalance. Early recognition enables timely intervention and improved outcomes. While nutrition and herbal medicine may support overall health, they must complement, not replace, medical care. Evidence-based guidance, regular screening, and professional consultation remain essential. This article is for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice.
Read Also: Ginseng for Blood Sugar Balance: Scientific Evidence, Benefits, and Safe Use
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Are diabetes symptoms always obvious?
No. Many people experience mild or unnoticed symptoms, especially in early type 2 diabetes.
Q2: Can diabetes symptoms go away on their own?
Symptoms may lessen with lifestyle changes, but diabetes requires medical management.
Q3: Are herbal remedies enough to control diabetes?
No. Herbs may support health but cannot replace medical treatment.
Q4: How soon should testing be done after symptoms appear?
Testing should be done as soon as possible to prevent complications.
Q5: Is fatigue always related to diabetes?
Not always. However, persistent fatigue with other symptoms warrants evaluation.
🇰🇷 Premium Korean Ginseng Online Shop