Heart disease remains one of the leading causes of illness around the world. Understanding its early symptoms is essential because many people do not realize they have a heart-related condition until it becomes serious. This article explains the common signs of heart disease, why they appear, and when to seek medical help—based on reputable health information sources and expert consensus.
What Is Heart Disease?
“Heart disease” refers to a range of conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels, including coronary artery disease, arrhythmias, heart failure, and congenital heart problems. These conditions may develop gradually over time, often without obvious symptoms at the beginning.
Recognizing early warning signs helps individuals get timely evaluation by health professionals.
Common Symptoms of Heart Disease
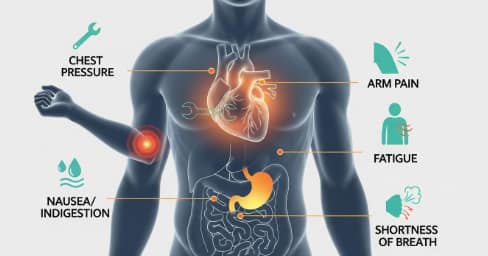
1. Chest Discomfort (Chest Pain or Pressure)
Chest discomfort is the most recognized sign of heart problems. It may feel like:
- Pressure
- Tightness
- Squeezing
- Burning
- A heavy weight
This sensation often occurs in the center or left side of the chest. Not all chest pain is heart-related, but persistent, unusual, or severe discomfort should always be evaluated by a medical professional.
2. Shortness of Breath
Shortness of breath during normal activities—or while resting—can be an early indicator of heart problems. This symptom may occur because the heart is not pumping efficiently, reducing oxygen delivery throughout the body.
3. Unusual Fatigue
Feeling extremely tired without a clear reason can be linked to heart disease, especially in women. It may occur days or even weeks before other symptoms.
4. Pain That Spreads to Other Areas
Heart-related discomfort can radiate to:
- Neck
- Jaw
- Shoulder
- Back
- Arms (usually the left arm)
This spreading pain is often associated with reduced blood flow to the heart.
5. Lightheadedness or Dizziness
Reduced blood circulation may cause dizziness. If dizziness happens together with chest discomfort or shortness of breath, it requires urgent medical attention.
6. Swelling in Legs, Ankles, or Feet
Fluid retention—known as edema—may occur when the heart struggles to circulate blood efficiently. This is common in certain types of heart failure.
7. Irregular Heartbeat (Palpitations)
A heart that beats too fast, too slow, or irregularly may signal an underlying condition. Occasional palpitations can be normal, but frequent or persistent irregular rhythms should be checked by a healthcare provider.
Why Recognizing Symptoms Matters
Many heart conditions are silent until they reach an advanced stage. Early detection allows:
- Proper diagnosis by qualified medical professionals
- More effective medical treatment
- Reduced risk of complications
If you or someone you know experiences persistent or severe symptoms, seek medical evaluation promptly.
Who Is at Higher Risk?
People with the following factors may be more likely to develop heart disease:
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Family history of heart problems
- Sedentary lifestyle
- High stress levels
Everyone—whether at high risk or not—should pay attention to early warning signs.
When to Seek Medical Help
Seek immediate professional help if you experience:
- Sudden chest pain or pressure
- Shortness of breath that worsens
- Fainting or severe dizziness
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Pain spreading to jaw, arm, or back
Only healthcare professionals can diagnose heart disease through proper examinations, tests, and medical evaluation.
How to Support Heart Health (General Non-Medical Tips)
While only a doctor can give medical advice, many experts agree that healthy lifestyle choices support overall heart wellness. These include:
- Balanced eating patterns
- Regular physical activity
- Managing stress
- Avoiding tobacco
- Regular health check-ups
Always consult a qualified healthcare provider before making significant lifestyle changes if you have existing health concerns.
Conclusion
Heart disease symptoms can appear slowly or suddenly. By understanding the early signs—such as chest discomfort, shortness of breath, and unusual fatigue—you can take proactive steps toward protecting your heart health. Awareness, combined with professional medical evaluation, plays a key role in preventing more serious complications.