Overview
Korean red ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) is one of the most extensively studied botanical adaptogens in immunology and clinical phytotherapy. Traditionally prescribed to enhance vitality and resilience, modern biomedical research now investigates its effects on immune regulation, cytokine balance, natural killer cell activity, T-cell activation, antibody production, and immunometabolic pathways.
Unlike synthetic immunostimulants, Korean red ginseng appears to act as a bi-directional immune modulator, meaning it helps the immune system adapt to stressors and maintain homeostasis — supporting low immune function while potentially regulating excessive inflammation.
⚠ Medical Disclaimer: Korean red ginseng does not prevent or cure viral or bacterial infections. It is not a substitute for medical treatment, vaccination, or professional healthcare guidance.
Understanding the Immune System
To understand how Korean red ginseng affects immunity, it’s important to first understand basic immune physiology.
Two Main Branches of Immunity
1. Innate (non-specific) immunity
- First response (minutes to hours)
- Includes macrophages, NK cells, neutrophils
- Uses pattern recognition receptors (PRRs)
- Controls early infection before antibodies form
2. Adaptive (specific) immunity
- Slower response, highly targeted
- Requires antigen presentation
- Involves T-cell & B-cell activation
- Generates immunological memory
📎 Overview reference
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK26827/
Korean red ginseng has been studied for its effects on both systems.
Mechanisms of Korean Red Ginseng in Immune Regulation
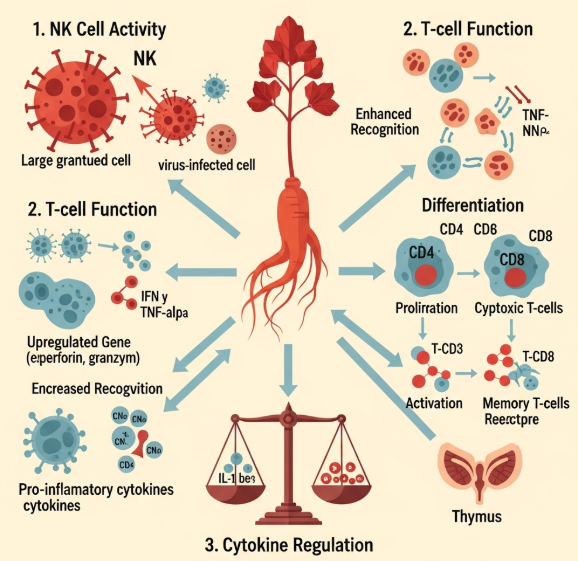
2.1 Natural Killer (NK) Cell Activity
NK cells are frontline immune cells that eliminate virus-infected and abnormal cells.
Korean red ginseng has demonstrated the ability to:
✔ Increase NK cell cytotoxicity
✔ Support interferon production
✔ Improve NK cell receptor sensitivity
📎 Clinical study
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16822204/
2.2 Macrophage Activation
Macrophages coordinate both innate and adaptive immunity through:
- Phagocytosis
- Antigen presentation
- Cytokine signaling
Ginsenosides upregulate TNF-α, IL-1β, and nitric oxide when needed — supporting pathogen defense without overstimulation.
2.3 Adaptive Immune Support (T & B cells)
Korean red ginseng has been shown to influence:
- CD4+ helper T cell activation
- CD8+ cytotoxic T cell response
- B-cell antibody synthesis
- Treg-mediated immune balance
📎 Study on immune modulation & antibodies
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18446268/
2.4 Vaccine Response Enhancement
A randomized controlled trial found that red ginseng enhanced antibody response to influenza vaccination and reduced incidence of respiratory illness.
📎 Clinical evidence
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11718077/
This suggests ginseng may help support immune system resilience, particularly in older adults.
2.5 Anti-inflammatory & Cytokine Modulation
Ginseng influences cytokine production including:
- IL-6
- IL-10
- TNF-α
- IFN-γ
Unlike immune stimulators that induce inflammation, red ginseng helps normalize cytokine levels depending on immune conditions — a key principle in immunomodulation.
📎 Review
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3659612/
2.6 Impact on Immunometabolism
New research links immunity to metabolic energy pathways. Ginsenosides may:
- Support mitochondrial efficiency
- Reduce oxidative stress
- Balance immune energy utilization
This is particularly important in chronic fatigue, long-term stress, viral recovery, aging, and metabolic syndromes.
Clinical Evidence Summary
| Study | Type | Participants | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scaglione et al., 1994 | RCT | 227 adults | Reduced infections vs placebo |
| Ota 2012 | RCT | Elderly | Increased NK activity |
| Lee et al. 2012 | Trial | 90 adults | ↑ immune cells & ↓ oxidative stress |
| Jung 2019 | Trial | 100 adults | Better immunity & lower fatigue |
| Rhee 2009 | Review | 30+ trials | Overall immune-enhancing trend |
Comparison With Other Immune Supplements
| Supplement | Immune Effect | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C | Antioxidant | Short-acting |
| Zinc | Antiviral metabolism | GI upset |
| Echinacea | Innate immunity | Not for long-term |
| Probiotics | Gut-mediated immunity | Strain-dependent |
| Korean Red Ginseng | Bi-directional immune modulation | Works gradually |
Ginseng can be paired with these supplements for synergistic effects.
Who May Benefit?
✔ Older adults with decreased immune function
✔ People under chronic stress
✔ Individuals with poor sleep and fatigue
✔ Frequent travelers
✔ Athletes in intensive training
✔ People seeking seasonal immune maintenance
⚠ Safety, Side Effects, and Contraindications
Generally well tolerated. Possible mild effects:
- Insomnia
- Digestive upset
- Headache
- Mild nervousness
Avoid or use cautiously in:
❌ Autoimmune disease (unless supervised)
❌ Organ transplant patients
❌ Those on immunosuppressive medications
❌ Warfarin / anti-coagulant users
❌ Pregnant individuals without medical advice
Safe duration in studies: up to 3 months of continuous use.
🧠 FAQ
Does Korean red ginseng replace vaccines?
No. It may support immune response but does not replace vaccination.
Is it safe for children?
Not recommended unless approved by a healthcare practitioner.
Can it be used for autoimmune disease?
It depends — use only under medical supervision.
Is fermented ginseng better for immune support?
Fermented red ginseng improves ginsenoside absorption and may have enhanced immune activity.
How long before effects are noticeable?
Immune benefits generally develop in 4–8 weeks.
🧬 Summary
Korean red ginseng is one of the most scientifically validated herbal immunomodulators, with clinical, biochemical, and mechanistic research supporting its role in immune balance, anti-inflammatory signaling, and adaptive response.
It is useful as a preventive wellness supplement, not a medical treatment.