Migraines are more than just severe headaches—they are complex neurological events that can significantly disrupt daily life. For millions of people worldwide, migraines present recurring challenges that demand thoughtful management strategies grounded in medical expertise, lifestyle choices, and self-care techniques. In this article, we explore evidence-based approaches to managing migraines, offering actionable insights that align with Google’s E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) framework.
Understanding Migraines
Migraines are typically characterized by intense throbbing pain, often on one side of the head, and can last anywhere from a few hours to several days. They are frequently accompanied by additional symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light or sound. According to the World Health Organization, migraines are one of the leading causes of disability worldwide, highlighting the importance of effective treatment and prevention.
Migraines can be triggered by a range of factors including stress, hormonal changes, dehydration, certain foods, or irregular sleep. Understanding these triggers is crucial for personalized management.
Core Strategies for Migraine Management
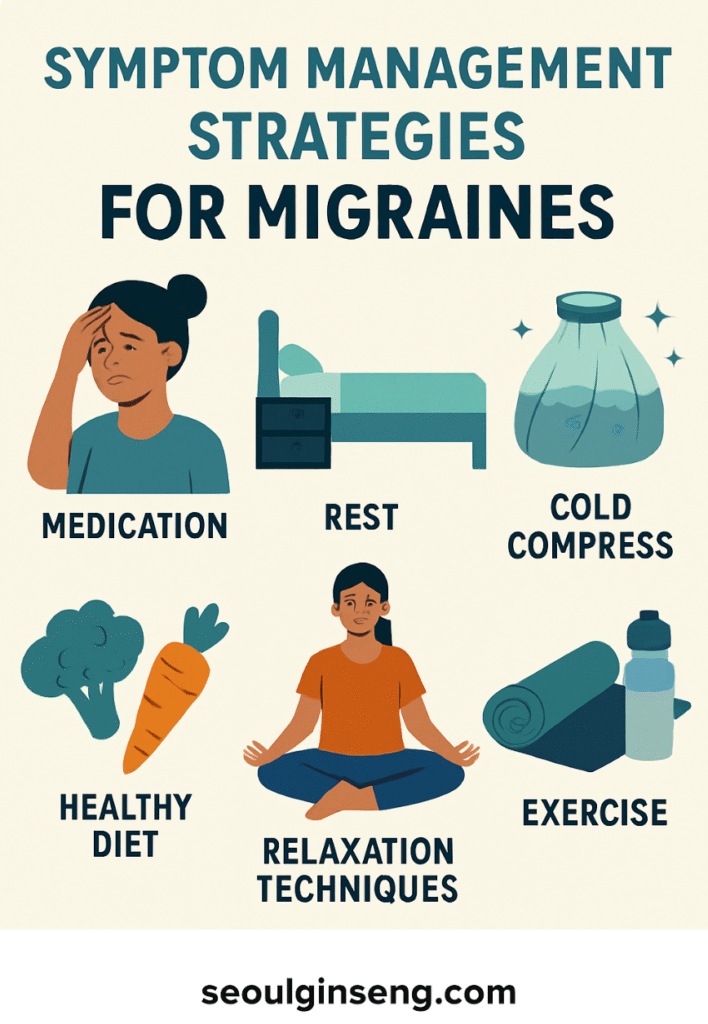
1. Medication
Modern medicine provides effective options for both acute migraine relief and long-term prevention. Over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen may help in mild cases, while prescription drugs—including triptans and preventive beta-blockers—are essential for severe or chronic cases. Consulting with a healthcare professional ensures the most effective and safe use of medication.
2. Rest and Sleep Hygiene
Adequate rest is essential during an active migraine episode. Lying in a quiet, dark room often provides relief. Long-term, maintaining good sleep hygiene—such as going to bed and waking up at consistent times—can significantly reduce the frequency of migraines.
3. Cold Compress Therapy
Applying a cold compress to the head or neck can constrict blood vessels and numb pain. Many patients report significant relief with this simple, non-invasive technique.
4. Nutrition and Hydration
Diet plays a central role in migraine prevention. Avoiding known triggers such as processed meats, artificial sweeteners, and excessive caffeine is essential. Staying hydrated—by drinking enough water throughout the day—helps minimize the risk of dehydration-induced migraines.
5. Relaxation and Stress Management
Stress is one of the most common migraine triggers. Techniques such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, and deep-breathing exercises can help reduce tension and promote relaxation. Studies have shown that cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is also highly effective in reducing migraine frequency.
6. Exercise and Physical Well-Being
Regular aerobic exercise promotes better blood flow and reduces stress, making it an excellent preventative strategy. Low-impact activities like walking, swimming, and cycling are particularly beneficial. However, overexertion should be avoided, as it can sometimes trigger migraines.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Long-Term Relief
- Consistent daily routine in meals, exercise, and sleep.
- Limiting screen time and ensuring proper eye care to avoid strain.
- Tracking symptoms with a migraine diary to identify and manage personal triggers.
Why This Matters
Migraines are a deeply personal health condition. What works for one person may not work for another. That’s why combining medical guidance with lifestyle strategies provides the most reliable path forward. By aligning treatment approaches with credible sources and clinical research, individuals can regain control over their lives and minimize the burden of recurring migraines.
🇰🇷 Premium Korean Ginseng Online Shop