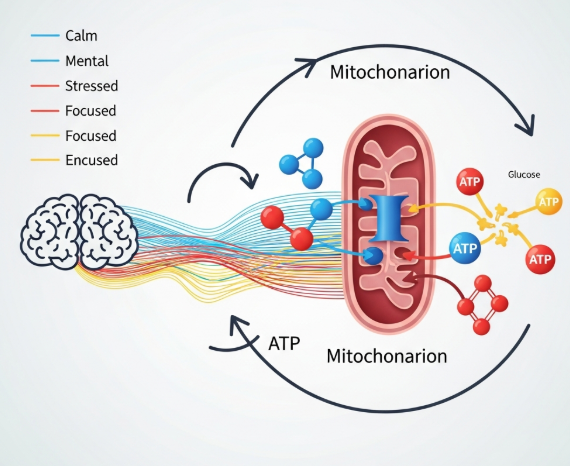
The mind and the body are often spoken of separately: thoughts reside in the brain, energy flows through the body. But modern research and centuries of traditional wisdom converge on one truth: your thoughts and emotions directly influence cellular energy production.
Every cell in your body depends on energy to function. Your mitochondria, often called the powerhouses of the cell, transform nutrients and oxygen into ATP—the currency of life. What many do not realize is that this cellular machinery is profoundly affected by mental and emotional states.
Stress, anxiety, or chronic negativity doesn’t just feel unpleasant; it subtly slows energy production, shifts metabolic pathways, and reduces resilience. Conversely, calm, focused, and positive mental states can enhance mitochondrial efficiency, improve nutrient utilization, and elevate overall vitality.
1. How Thoughts Affect Cellular Energy
Neurons communicate constantly with the rest of the body through chemical signals. This communication isn’t just metaphorical—it has measurable metabolic effects:
- Stress hormones (cortisol, adrenaline): Short-term, they increase energy temporarily. Chronic release, however, overwhelms cells, depletes ATP, and increases oxidative stress.
- Neurotransmitters (serotonin, dopamine): Affect not only mood but also metabolic pathways in muscles, liver, and even heart cells.
- Mindset signals: Focus, purpose, and emotional clarity can improve energy efficiency by optimizing parasympathetic activation during rest and recovery phases.
Essentially, your mental landscape shapes your cellular environment.
2. Emotional States and Metabolic Shifts
Different emotions have distinct metabolic footprints:
- Anxiety or chronic worry: Increases inflammation, diverts energy to survival processes, reduces regenerative efficiency.
- Depression or emotional fatigue: Lowers mitochondrial output, diminishes neural signaling, slows energy release.
- Calm, joy, and gratitude: Promote parasympathetic dominance, enhance nutrient uptake, and optimize energy production.
Even subtle mental shifts—like micro-stress from notifications or low-level mental clutter—can influence cellular function over time.
3. Energy Flow and Mood
Your body’s energy level is directly tied to how your cells perceive and respond to internal signals:
- Mental clarity depends on neurons receiving sufficient ATP to maintain synaptic firing.
- Motivation relies on dopamine pathways functioning optimally, which are sensitive to oxidative stress and mitochondrial efficiency.
- Fatigue often reflects cellular energy deficits before it manifests in the muscles or organs.
Hidden fatigue, low motivation, or mood swings are often metabolic signals triggered by the mind rather than only lifestyle factors.
4. How to Harmonize Mind and Metabolism
Supporting your mind–metabolism connection doesn’t require extreme intervention—it’s about rhythm, awareness, and consistency:
1. Mindful Breathing and Meditation
Deep, intentional breathing increases oxygen delivery, reduces cortisol, and signals cells to switch from survival mode to regenerative mode.
2. Mental Clarity Practices
Journaling, visualization, or even short breaks to reset focus can reduce micro-stress that quietly drains cellular energy.
3. Physical Activity Aligned with Mind
Movement synchronized with awareness—like yoga, tai chi, or gentle walking—improves circulation, enhances mitochondrial efficiency, and reduces inflammation.
4. Balanced Nutrition
Cells require antioxidants, B-vitamins, magnesium, and omega-3s to maintain energy. Nutritional support enhances the body’s ability to translate positive mental signals into energetic efficiency.
5. Sleep with Intention
Sleep isn’t just rest—it’s metabolic repair. Reducing mental clutter before sleep improves mitochondrial regeneration and restores ATP levels.
5. The Feedback Loop: Energy Shapes Thought
The relationship is not one-way. Just as thoughts affect cellular metabolism, cellular energy influences thoughts:
- Low energy can make focus and problem-solving difficult.
- Fatigue may amplify negative thinking patterns.
- Optimized metabolism enhances clarity, motivation, and emotional resilience.
In essence: energy and mind are a continuous feedback loop, each influencing and amplifying the other.
6. Integrating Mind-Metabolism Awareness into Daily Life
- Start the day with 5 minutes of mindful breathing.
- Take micro-breaks every 90–120 minutes to reset focus and reduce metabolic stress.
- Include nutrient-rich, anti-inflammatory foods in every meal.
- Observe how emotional patterns influence physical energy, and adjust routines accordingly.
By creating harmony between your mind and metabolism, energy becomes steady, mood stabilizes, and productivity aligns naturally with well-being.