Can Korean Red Ginseng Support Insulin Sensitivity?
Insulin sensitivity refers to how effectively your cells respond to insulin, the hormone responsible for glucose uptake and energy regulation. Reduced sensitivity, or insulin resistance, is a key factor in metabolic syndrome, prediabetes, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular risk.
Korean Red Ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) has been studied for its potential to support insulin signaling, improve glucose utilization, and modulate metabolic pathways — helping the body maintain healthier blood sugar balance naturally.
⚠ Disclaimer: Korean Red Ginseng does not replace prescribed medication. It may support healthy insulin function as part of a holistic lifestyle plan.
Understanding Insulin Sensitivity
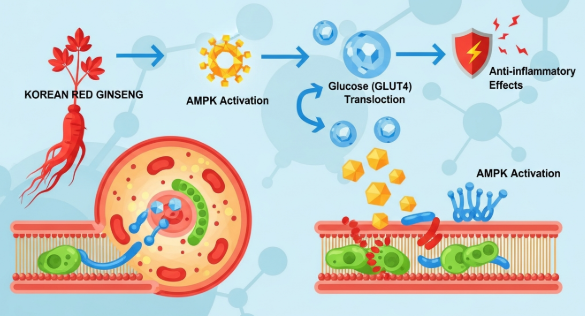
- Insulin binds to receptors on muscle, liver, and fat cells.
- This triggers GLUT4 transporter translocation to the cell membrane.
- Glucose enters cells to be used for energy or stored.
- Chronic stress, poor diet, obesity, and inflammation can impair insulin signaling, leading to insulin resistance.
How Korean Red Ginseng May Support Insulin Sensitivity
1. Enhanced Insulin Receptor Signaling
Ginsenosides such as Rb1, Rg1, and Re may:
- Increase phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrates (IRS-1, IRS-2)
- Activate the PI3K/Akt pathway
- Improve GLUT4 translocation in muscle and adipose tissue
📎 Reference:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24399212/
2. AMPK Activation & Cellular Energy Balance
- AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) is a key energy sensor in cells.
- Red ginseng may stimulate AMPK, leading to:
- Enhanced glucose uptake
- Increased fatty acid oxidation
- Reduced lipid accumulation
📎 Reference:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22814660/
3. Anti-Inflammatory & Oxidative Stress Effects
Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress impair insulin signaling. Red ginseng helps:
- Reduce TNF-α and IL-6
- Decrease reactive oxygen species
- Protect insulin receptor function
📎 Reference:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3659612/
4. Gut Microbiome Modulation
Emerging studies show that fermented Korean red ginseng may alter gut microbiota favorably, producing metabolites that improve insulin sensitivity.
📎 Reference:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31347025/
Clinical Evidence
| Study | Participants | Intervention | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vuksan et al., 2000 | Type 2 diabetes | 3 g/day red ginseng | ↑ insulin sensitivity, ↓ fasting glucose |
| Reay et al., 2009 | Healthy adults | 2 g/day | ↓ postprandial glucose |
| Shin et al., 2013 | Prediabetes | 3 g/day | ↑ insulin sensitivity markers |
| Park et al., 2019 | Fermented red ginseng | 2 g/day | ↓ HOMA-IR, improved HbA1c |
Dosages in studies typically ranged 1–3 g/day, over 4–12 weeks.
Who May Benefit
✔ People with insulin resistance or prediabetes
✔ Individuals aiming for better post-meal glucose control
✔ Those seeking metabolic flexibility and energy efficiency
✔ Active adults or athletes
✔ Aging individuals at risk for metabolic syndrome
Red ginseng is not a replacement for diabetes medication and should be used under supervision.
Safety & Side Effects
- Generally well tolerated
- Mild effects: insomnia, digestive upset, nervousness
- Interactions possible with insulin or oral hypoglycemics — monitor glucose
- Safe duration in clinical trials: 4–12 weeks
Recommended Use
- Standardized extract: 1,000–3,000 mg/day
- Morning or early afternoon dosing
- Fermented red ginseng may improve absorption and efficacy
FAQ
Q: How does red ginseng improve insulin sensitivity?
A: Through insulin receptor signaling enhancement, GLUT4 translocation, AMPK activation, and anti-inflammatory effects.
Q: How long until effects are seen?
A: Some benefits appear in 2–4 weeks; optimal results often require 8–12 weeks.
Q: Can it be combined with diabetes medication?
A: Yes, under medical supervision to avoid hypoglycemia.
Q: Is fermented ginseng better?
A: Yes — fermentation increases ginsenoside absorption and metabolic impact.