Home | Shop | Learn About Ginseng | Ginsenoside per Product | Blog | Our Story | Refer & Earn | Contact Us | Cart | Checkout | My Account





Korean Wild Ginseng: A Promising Natural Solution for Reducing Insulin Resistance
Korean wild ginseng, long celebrated in traditional medicine, is now emerging as a powerful natural remedy for reducing insulin resistance. With the prevalence of metabolic disorders and type 2 diabetes on the rise, research into alternative therapies is gaining momentum. Korean wild ginseng, known for its potent bioactive compounds, offers a unique approach to improving insulin sensitivity and regulating blood sugar levels.
Introduction to Insulin Resistance and Korean Wild Ginseng
Insulin resistance occurs when the body’s cells fail to respond effectively to insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels and increased risk for type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and metabolic syndrome. For centuries, Korean wild ginseng (산삼) has been a staple in Eastern herbal medicine, renowned for its ability to enhance energy, improve vitality, and promote overall wellness. Recent studies suggest that this ancient herb may also play a crucial role in reducing insulin resistance and improving metabolic health.
Historical Background and Traditional Uses
Korean wild ginseng has been an integral part of traditional Korean medicine for millennia. Traditionally, it was used to boost the immune system, enhance physical stamina, and balance the body’s internal functions. Healers and herbalists valued wild ginseng not only for its rejuvenating properties but also for its perceived ability to regulate various physiological processes—including those related to blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity.
Scientific Evidence and Research Findings
Modern scientific research is beginning to validate the traditional uses of Korean wild ginseng, particularly in relation to metabolic health. Several preclinical studies have demonstrated that ginseng extracts can significantly improve insulin sensitivity. Key findings include:
Enhanced Insulin Signaling:
Bioactive compounds in Korean wild ginseng, such as ginsenosides, have been shown to improve the efficiency of insulin signaling pathways. By enhancing the responsiveness of cells to insulin, these compounds help lower blood glucose levels.Reduction of Inflammatory Markers:
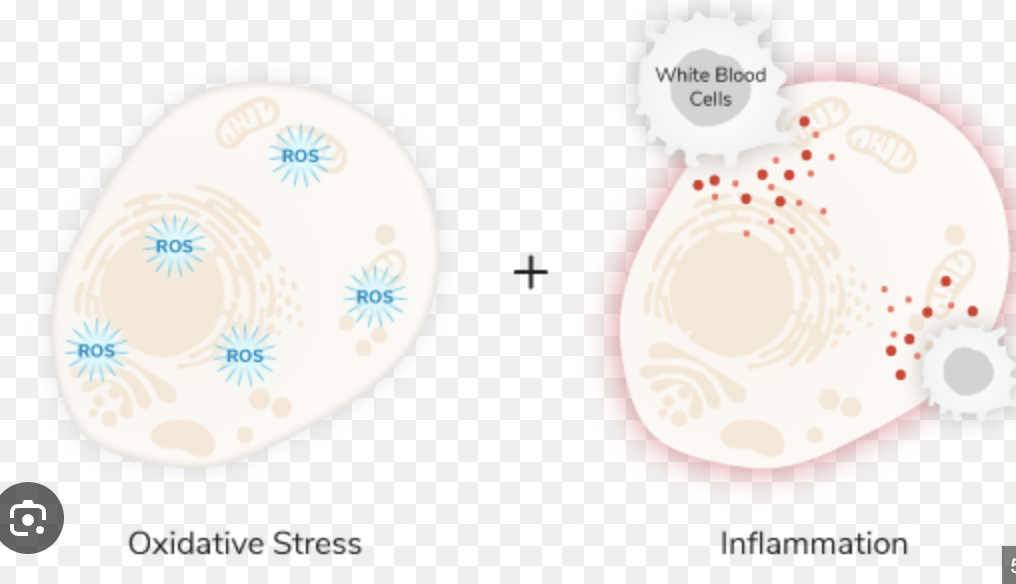
Chronic inflammation is a major contributor to insulin resistance. Research indicates that the anti-inflammatory properties of Korean wild ginseng help reduce levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, thereby mitigating inflammation and improving insulin action.Antioxidant Effects:
Oxidative stress, resulting from an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants, plays a key role in the development of insulin resistance. Korean wild ginseng is rich in antioxidants that protect cells from oxidative damage, thus supporting healthier metabolic function.Regulation of Glucose Metabolism:
Studies have found that ginseng can influence key enzymes involved in glucose metabolism, leading to improved blood sugar control and a reduction in insulin resistance over time.
Mechanisms of Action
The beneficial effects of Korean wild ginseng on insulin resistance are thought to be mediated through several biological mechanisms:
Ginsenosides and Insulin Sensitivity:
Ginsenosides, the primary active constituents in ginseng, have been shown to enhance insulin receptor sensitivity and stimulate glucose uptake in muscle and adipose tissues.Anti-Inflammatory Response:
By reducing the production of inflammatory cytokines, Korean wild ginseng helps create a more favorable environment for insulin to function effectively.Antioxidant Protection:
The potent antioxidants in ginseng combat oxidative stress, preserving the integrity of insulin receptors and supporting overall cellular health.Modulation of Metabolic Enzymes:
Korean wild ginseng influences enzymes that regulate glucose and lipid metabolism, contributing to improved energy balance and reduced insulin resistance.
Clinical Implications and Practical Applications
The promising results from preclinical studies have paved the way for clinical trials examining the effects of Korean wild ginseng on insulin resistance in humans. Early clinical findings suggest that regular supplementation with high-quality ginseng extracts may lead to:
- Improved insulin sensitivity and lower fasting blood glucose levels.
- Reduced markers of inflammation and oxidative stress.
- Enhanced overall metabolic health, contributing to better management of type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
For individuals looking to incorporate Korean wild ginseng into their health regimen, it is important to choose reputable products and consult healthcare professionals—especially those managing diabetes or other metabolic disorders.
Future Directions and Ongoing Research
Ongoing research aims to further elucidate the molecular pathways through which Korean wild ginseng exerts its effects on insulin resistance. Future studies will focus on:
- Establishing optimal dosages and formulations.
- Long-term safety and efficacy in diverse populations.
- Potential synergistic effects when combined with other natural supplements or lifestyle interventions.
These investigations will provide deeper insights into how Korean wild ginseng can be effectively integrated into comprehensive strategies for managing insulin resistance and improving metabolic health.
Conclusion
Korean wild ginseng represents a promising natural intervention for reducing insulin resistance and enhancing metabolic health. Through its multifaceted actions—ranging from improving insulin signaling and reducing inflammation to providing robust antioxidant protection—this ancient herb offers a holistic approach to managing blood sugar levels and preventing type 2 diabetes. As modern research continues to validate its benefits, Korean wild ginseng is poised to become an integral part of natural health strategies aimed at combating metabolic disorders.
#koreanwildginseng, #insulinresistance, #diabetesprevention, #metabolichealth, #herbalmedicine, #naturalremedy, #bloodsugarcontrol, #ginsenosides, #antioxidants, #inflammation








Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.